According to the American College of Allergy, Asthma, and Immunology, approximately 20% of Americans suffer from some kind of allergy, making it the fifth-most prevalent chronic health condition in the country. The first step is to understand exactly what types of allergies are making you suffer the most.
What is Allergy Testing?
An allergy is when your body's immune response, which is your body's natural defense, overreacts to something in your environment. Allergens include substances you eat, inhale, or touch that your immune system perceives as "foreign invaders." Some of the common symptoms related to allergy are:
- Itchy, red, watery eyes
- Runny, itchy, or blocked nose with sneezing
- Rashes, reddened and cracked skin
- Nausea, diarrhea, vomiting, and stomach pain
- Coughing, wheezing, chest tightness, and shortness of breath
- Swelling of the lips, tongue, eyes, or face
One must undergo allergy testing to uncover what triggers these symptoms. It is a test done by a trained allergy specialist to determine if your body is allergic to pollen, mold, medicine, food, and many more substances. In the course of the test, you will be exposed to specific allergens signs then the attending physician will observe any allergic reactions.
Different Types of Allergy Testing
There are numerous types of tests that allergy specialists can conduct. Others require testing your blood, while others test the skin for reactions. Here are the different ways of testing for allergies:
Skin Prick Test
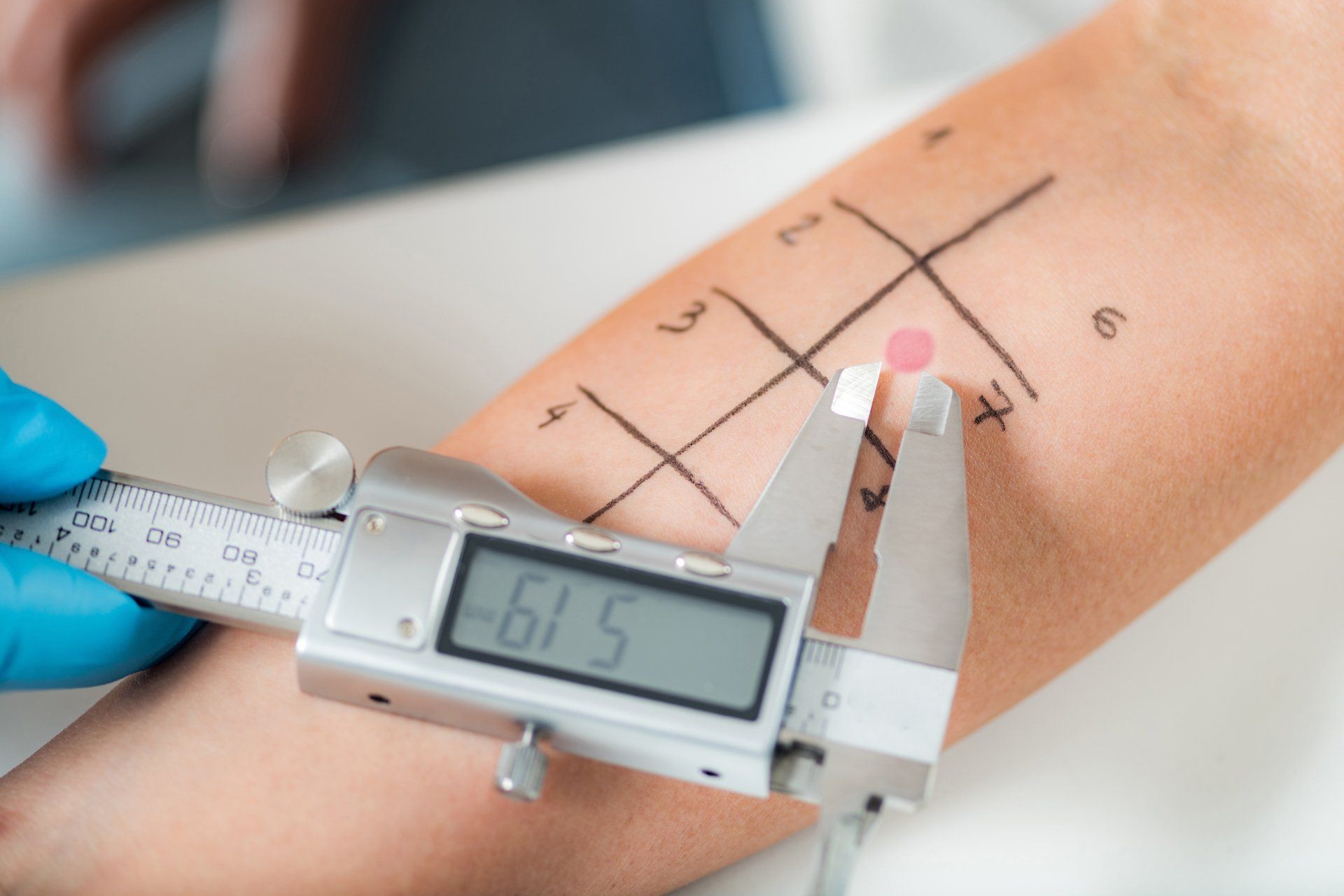
The skin prick test involves applying a solution containing an allergen to the skin and allowing the sample to seep into the skin through scratches or needle pricks. When the skin develops an itchy red (called a wheal), it's typically a sign that the person is allergic to that allergen. To determine if an actual allergic reaction occurred, the allergist compares the wheal diameter to the controls.
Intradermal Skin Test
Unlike skin prick tests, intradermal skin tests involve injecting a small amount of allergen into the skin. The test is more sensitive than the skin prick. An intradermal test may be recommended if your skin prick test is negative. Typical allergens tested intradermally are venom and penicillin.
Skin Allergy Patch Test
The allergy patch test involves placing allergen solution on a pad and applying it to the skin for 24-72 hours. Skin allergies such as contact dermatitis can be diagnosed with this test.
Blood Allergy Tests (Specific IgE)
The purpose of allergy blood tests is to detect antibodies in the blood. People who cannot undergo skin tests can take blood tests. Blood tests are less sensitive than skin tests.
Blood tests are suitable for people who have skin conditions, are on a medicine that interferes with skin testing, or are taking a medicine that interferes with skin testing. These tests are also appropriate for children who may not tolerate skin testing.
The doctor will collect a blood sample and send it to a laboratory for analysis. Your blood sample becomes exposed to the allergens, and the lab then determines the number of antibodies your blood produces to attack those allergens. This test is called Specific IgE (sIgE) Blood Testing (previously and commonly referred to as RAST or ImmunoCAP testing).
Physician-Supervised Challenge Tests
A doctor will administer a tiny dose of an allergen to you by oral intake or inhaling it. Usually, this test is in conjunction with a possible food allergy or medication. Testing is only possible under the supervision of an allergist/immunologist and with immediate resuscitation facilities readily available.
Elimination Diet
For 2-4 weeks, you will abstain from eating certain foods that you suspect are allergens. If your allergy symptoms subside during this period, one or more of the eliminated foods most likely was the cause of your problems.
Spirometry Lung Function Test
Its use is to diagnose asthma-related issues. There have been studies that have shown the majority of asthma patients have the most allergies. The spirometry test requires you to breathe deeply and to exhale quickly and forcefully several times. The procedure measures your lung function, which is vital for further diagnosis.
Frequently Asked Questions about Allergy Testing
How Should I Prepare for Allergy Testing?
At least five days before the appointment, you should stop using antihistamines. Studies have shown that antihistamines affect test results. Read more on what to do prior to allergy testing.
How is Allergy Testing Done?
The doctor will begin by taking a detailed history of your symptoms and other relevant aspects of your medical background. The doctor will then perform a physical examination. After reviewing your medical history and exam findings, the physician determines whether you require further testing and exactly what kind of allergy testing you need.
How Long Does Allergy Testing Take?
Not all allergy testing has the same timeframe. Here's a typical timeframe for each test.
- Skin Prick and Intradermal Test: 15-20 minutes
- Skin Patch Test: Allergen solution must be placed on the skin for 24-72 hrs. Results usually take between 2-5 days to appear.
- Elimination Diet: 2-4 weeks of avoiding certain foods
- Most will take an hour or less but the release time of results will vary
Are at-home allergy tests effective?
According to the American Association of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology (AAAI), allergy testing kits are neither useful nor effective. World Allergy Organization (WAO) also discourages home allergy testing mainly because of the potential for misdiagnosis.
Take Control of Your Allergies
It is critical to know whether you are allergic to something so that you can take the proper precautions. Understanding what triggers your allergy allows you to avoid those substances. You don't have to be controlled by allergies, so take charge of them today.
Board-certified allergist and immunologist
Dr. Sabharwal specializes in diagnosing and treating pediatric and adult allergies. She offers individualized allergy treatment plans to alleviate your symptoms. Get in touch with Allergy Affiliates and schedule a
consultation today.