Do you find yourself coughing persistently for weeks or even months? If so, you may be experiencing a chronic cough. Unfortunately, persistent coughing happens to people of all ages worldwide. Recent statistics from the National Institutes of Health say that out of 74,000 respondents, 3,654 reported experiencing chronic cough in the past 12 months.
Persistent coughing is more than just a nuisance. It negatively impacts the time spent with your loved ones, work productivity, school performance, or daily chores. If you notice a decline in your quality of life due to chronic coughs, understanding its causes, symptoms, and diagnosis is more important than ever.
We recommend consulting your healthcare provider if your cough persists for over eight weeks. In the meantime, let’s answer some of your questions about chronic cough.
Why Am I Coughing Constantly?
Various factors contribute to chronic cough development. Some are due to pre-existing conditions (asthma or bronchitis) that exacerbate the symptoms over time. Other causes come from medication side effects and environmental triggers. Here are the most common chronic cough causes:
Respiratory Infections
Recurring respiratory conditions, such as pneumonia or bronchitis, are the usual suspects. These infections irritate the airways, causing a persistent cough even after the infection has cleared.
Asthma
Asthma is a lifelong illness that often causes airway inflammation, leading to coughing, wheezing, and shortness of breath. Coughing is a predominant symptom in some cases.
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)
GERD occurs when bile (stomach acid) flows back into the esophagus. This condition irritates the throat and may lead to a chronic cough, often worse at night or after meals.
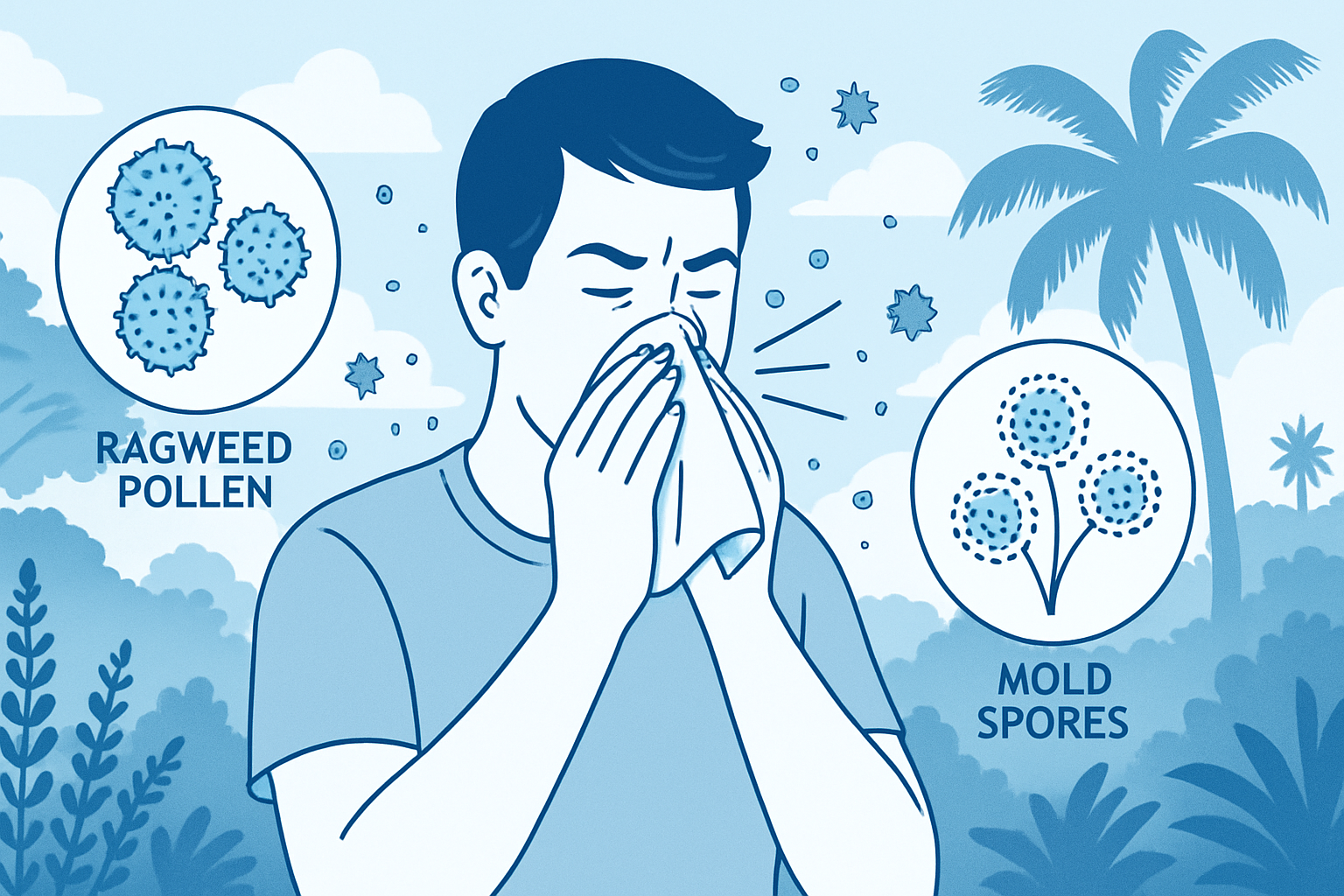
Postnasal Drip
Excess mucus production in the back of the throat due to allergies, sinusitis, or other nasal conditions can trigger a persistent cough.
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)
COPD encompasses conditions like chronic bronchitis and emphysema. These conditions lead to persistent inflammation in the airways, resulting in chronic coughing.
Medication Side Effects
Certain medications, particularly those for high blood pressure, may cause chronic cough as a side effect.
Environmental Irritants
Exposure to tobacco smoke, pollution, or workplace chemicals can cause chronic
coughs, particularly in those sensitive to these irritants.
What Are the Typical Signs and Symptoms of Chronic Cough?
The symptoms of chronic cough vary depending on the underlying cause, but typical signs include:
- Coughing constantly for eight weeks or more
- Coughing that worsens at night or early in the morning
- Wheezing or a whistling sound when breathing
- Shortness of breath
- Chest pain or discomfort
How Do Doctors Diagnose Chronic Cough?
Accurate diagnosis of what causes your chronic cough is crucial for effective treatment. From the initial consultation to planning the appropriate treatment options, your doctor will provide what you need to manage this medical condition effectively.
Medical History and Physical Examination
Your healthcare provider will begin by discussing your medical history and completing a physical examination. This approach will help identify potential causes and rule out certain conditions.
Chest X-Ray or CT Scan
Imaging tests like chest X-rays or CT scans are necessary for checking any abnormalities in the lungs or airways.
Pulmonary Function Tests
These tests evaluate lung function and can help identify conditions like asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
Allergy Testing
Skin or blood tests help identify specific allergens if allergies are suspected. The results allow your doctor to provide the proper medications and lifestyle adjustments for better outcomes.
Esophageal pH Monitoring
This test can help determine if GERD is a contributing factor by measuring the acidity in the esophagus. Chronic cough causes esophagus irritation that may lead to inflammation.
Bronchoscopy
In some cases, your doctor may suggest bronchoscopy. This procedure involves using a thin tube with a camera to examine the airways for abnormalities.
What Are the Medicines That Help Improve Chronic Cough?
Various medications are available to treat chronic cough, depending on the root cause.
Here are some common drugs that alleviate constant coughing symptoms:
1. Antihistamines:
These drugs block
histamine, a chemical that causes allergy symptoms like coughing and sneezing.
Antihistamines help improve coughs caused by allergies.
2. Decongestants: Decongestants help relieve nasal congestion and reduce mucus production. They are often effective for coughs caused by postnasal drip.
3. Bronchodilators: These
drugs help relax the muscles around the airways, making breathing easier. They commonly address coughs caused by asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
4. Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs): PPIs are suitable to manage gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), which can cause a chronic cough. They work by reducing the amount of acid produced by the stomach.
5. Corticosteroids: These drugs reduce inflammation in the airways and are often used to treat coughs caused by asthma.
6. Cough suppressants: These drugs reduce the urge to cough. They work well for dry, non-productive coughs.
Remember, always take medications under the guidance of a healthcare professional and only as prescribed. Some medicines may have side effects or interact with other drugs, so following your doctor's instructions is crucial.
Understanding chronic cough's underlying causes and symptoms is the first step toward effective management and relief. If you experience persistent coughing, seek prompt medical attention and obtain a proper diagnosis.
Early intervention prevents potential complications and significantly improves your quality of life. Feel free to consult a healthcare professional for personalized advice and treatment options.
FAQs
Q: What are the treatment options for chronic cough?
Treatment depends on the underlying cause. It may include:
- Root Cause Identification: Treating the primary cause, such as asthma, GERD, or allergies.
- Lifestyle Changes: Avoiding triggers like smoking, allergens, or other irritants.
- Anti-Allergy Medications: Depending on the underlying cause, your doctor may use antihistamines, bronchodilators, or proton pump inhibitors.
- Cough Suppressants: In some cases, cough suppressants can provide relief.
- Therapies: Speech therapy or techniques like breathing exercises can be helpful.
Q: When should I seek medical attention for a chronic cough?
You should see a doctor if:
- Your cough persists for over eight weeks (adults) or four weeks (children).
- You have difficulty breathing or chest pain.
- You cough up blood or experience unexplained weight loss.
Q: Are there any lifestyle changes that can help with a chronic cough?
Yes, chronic cough can improve with lifestyle changes such as:
- Avoiding Smoking: If you smoke, quitting can significantly reduce coughing.
- Avoiding Triggers: Identify and prevent substances or environments that exacerbate your cough.
- Staying Hydrated: Drinking fluids soothes your throat and naturally improves your symptoms.
Your Journey To a Chronic Cough-Free Life Begins Here!
If you're searching online for "constant coughing symptoms" or "chronic cough reasons," you’re on the right page. We understand the challenges of living with chronic cough. That's why we are here to provide lasting relief and recovery!
Bradenton and Sarasota Allergist
Dr. Sabharwal and her team of board-certified allergists offer safe and efficient chronic cough treatment and management with a proven track record. Ensure a healthier and happier lifestyle by calling us at 941-792-4151 or scheduling an appointment
here.