Living with allergies can be pretty challenging. Just when you thought you survived one allergy season, another comes in. Allergies are a part of life that you need to accept. The key to a better lifestyle when living with allergies is proper education. It would help if you learned the most effective management tips and the things to avoid during allergy season.
We created this guide to help you reduce the risks of triggering allergic reactions for the entire year. We'll discuss the common symptoms of allergies and their causes from January to December. Our goal is to provide you with ample knowledge on dealing with seasonal allergies the right way.
However, before we continue, we want you to know the meaning of the word allergy. So, let's begin with its definition.
What is Allergy?
An allergy occurs when your immune system negatively reacts to harmless proteins. It tries to eliminate normal proteins by attacking them. What happens next is an allergic reaction. You'll experience symptoms like runny nose, clogged nose, watery eyes, sneezing, skin rash, or difficulty breathing.
Symptoms typically appear a few minutes after exposure to allergens but go away naturally. The severity ranges from mild to moderate. However, severe symptoms may require immediate medical attention like anaphylaxis.
Now that we've defined the meaning of allergy, let's proceed to our month-by-month allergy guide.
Here's our monthly guide on what you need to know about allergies in season.
Allergy Months
January
There's nothing much to do during winter than spending more time indoors. However, it also means more exposure to indoor allergens. Here are the allergens that increase the risks of triggering allergic reactions
- Dust mites
- Pet dander
- Mold
Aside from these three, some individuals may experience a rare allergic reaction called cold urticaria. This skin condition's symptoms are
- Hives
- Redness
- Itchiness
- inflammation
What to do
The best way to reduce the risks of triggering an allergic reaction during the colder season is to maintain a humidity of 40% inside the house. In addition, change your bed sheets, blankets, and pillowcases regularly. It eliminates dust mites effectively. A hot bath does the trick too.
February
Trees in some areas in the United States begin to produce pollen in February. Tree pollen is one of the most potent allergens that could trigger an allergic reaction. The trees that release large amounts of pollen include
- Cedar
- Alder
- Maple
- Hickory
- Elm
- Walnut trees
The common symptoms of February allergies
- Sneezing
- Congestion
- Itchy and watery eyes
What to do
Watch the local weather forecast to learn the pollen count. Stay at home when the pollen count is high. You can also wear a facemask when you go outside to prevent inhaling the tree pollen allergens. Moreover, wash your clothes when you get home. Learning what allergies are bad right now can help you live and breathe easier.
March
As winter transitions to spring, so does the allergy season. Aside from the rampant tree pollen, weeds and grasses begin to produce pollen too. What's more, spring comes early in some regions in the United States. Here are the weeds and grasses that you need to avoid
Grass
- Bahia
- Fescue
- Johnson
- Kentucky blue
- Timothy
- Bermuda
Weed
- Tumbleweed
- Pigweed
- Mugwort
- Cocklebur
- Russian thistle
- Ragweed
- Lamb's-quarters
- Sagebrush
- Burning bush
What to do
When the grass or weed pollen count is high, staying indoors is your best bet. Limit your activities indoors to prevent triggering an allergic reaction. In addition, keep your doors and windows closed, especially at night. These tips can keep allergies March at bay.
April
April rains bring spring allergies. The flowers, trees, weeds, and grasses begin to bloom. It only means that April increases the pollen count immensely. Watch out for insects too. These tiny critters could bite or sting - triggering an allergic reaction. Please don’t get caught when allergies are at their worst.
What to do
Avoid places with abundant growth of trees, flowers, grasses, or weeds. If you can't avoid them, limit your time in those areas. If you get bitten or stung by an insect, consult an allergist as soon as possible. Allergies from insect bites or stings may lead to anaphylaxis.
Note:
Anaphylaxis is a severe allergic reaction that could be fatal. The victim may experience a sudden drop in blood pressure and shock. In addition, they may experience difficulty breathing because of inflammation in the airways.
May
Trees, flowers, grasses, and weeds are still abundant in May. They may not be as many as the previous month, but they still produce significant amounts of pollen.
What to do
You can ease out a bit from the allergies in May, but watching out for allergy triggers would not hurt.
June
The temperature starts to become warmer in June. Unfortunately, grasses and weeds produce more pollen during this time of year.
What to do
Warm weather is perfect for outdoor activities. However, you should limit your time outside if you have allergies. Try indoor sports or activities instead. You can still have fun inside the house if you know where to begin. You can manage allergies in June by following these tips.
July
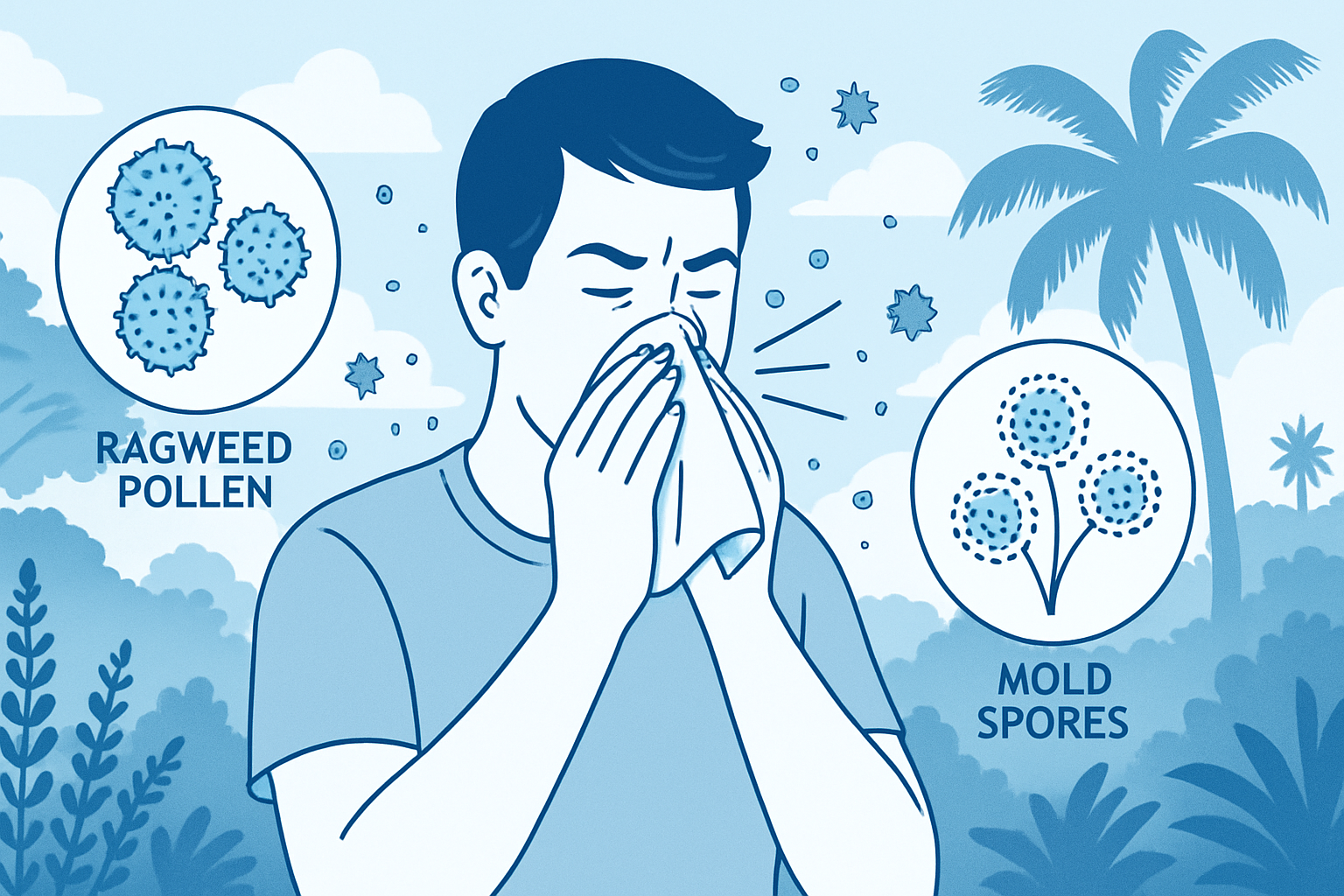
Good news! July is when trees and grass pollen levels begin to drop. However, molds begin to build up. Allergies from mold could trigger the symptoms of asthma. July allergies are less, so you can take a breather this month.
What to do
Clean the cold and damp areas of the house to eliminate mold growth. You can use household cleaning chemicals to get rid of them efficiently.
August
August is when molds are at their peak. This time, staying inside increases pollen exposure. Avoid allergies in August by keeping your house clean.
What to do
Good housekeeping is still the answer. In addition, prepare over-the-counter medicines to reduce allergy symptoms.
September
The allergies in September come from ragweed. Ragweed reaches its peak during these months. A single plant can produce billions of unseen pollen allergen into the air.
What to do
Learn the pollen count from your local weather channel. You can also download apps on your mobile device to keep track of the pollen count. With this information handy, you can reduce the risks of accidental exposure.
October
October once again brings good news. Fall allergies begin to cease in October. Watch out for mold buildup because of the occasional rains.
What to do
In October, you can avoid allergies by cleaning the cold, damp, and dark areas to prevent mold and fungi buildup.
November
November is when the overall pollen count declines. However, it also starts to become colder. Molds can still cause allergies. With fewer allergies in November, you can enjoy the season better.
What to do
Since you know what to do with mold buildup, we're pretty sure that November will be better for you.
December
Bringing a Christmas tree inside the house may be bad for individuals with tree pollen allergies. They could inhale the tree pollen and trigger an allergic reaction. In addition, cold urticaria could affect some people.
What to do
Use plastic trees instead of real ones. Use antihistamine to reduce the symptoms.
Know Your Allergies and Live a Better Life
Allergies can hit you anytime. It can catch you unaware if you're not prepared. Don't let it happen to you. Boost your immune system today. Bradenton and Sarasota Allergist Dr. Sabharwal can help you overcome seasonal allergies with proven and effective methods. Contact Allergy Affiliates at 941-792-4151 or book your appointment online by clicking on this link.