What is Angioderma?
Angioedema is a condition that causes the deeper layers of the skin to swell. This is due to an accumulation of fluid. It often manifests with angioedema lips or swelling of the tongue and throat.
When you have Angioedema, it usually appears within a few hours and
lasts for about a day or two. The situation could become quite serious if your throat swells up, interfering with your breathing. The right treatment and medication help maintain a more controllable swelling level that is less prominent or life-threatening.
Signs of Angioedema
The most prominent sign is a sudden swelling below the skin's surface. On the top of the skin, there is also the risk that swelling or welts will manifest themselves. It results from a fluid buildup in the body's tissues, typically affecting the area surrounding the eyes and mouth.
Angioedema symptoms
can also be seen on the hands, feet, and throat. The swelling can take the form of a line or be more scattered in its distribution.
The welts are excruciating, and there's a chance they'll also be bothersome. These are also known as hives in some circles (urticaria). They take on a pallid appearance and swell up when irritated, and their appearance changes. The deeper swelling caused by Angioedema will give you discomfort.
Additional symptoms include the
following:
- Eyes and lips puffy due to swelling
- Swollen eyelids and red (chemosis).
- Abdominal cramps
- Having trouble breathing
What Causes Angioedema?
When your immune system detects a potentially hazardous foreign substance known as an allergen, it triggers the production of the chemical histamine in your body.
Most patients will have difficulty identifying the underlying cause, but an allergy test may help. Here are the
following are potential triggers for Angioedema:
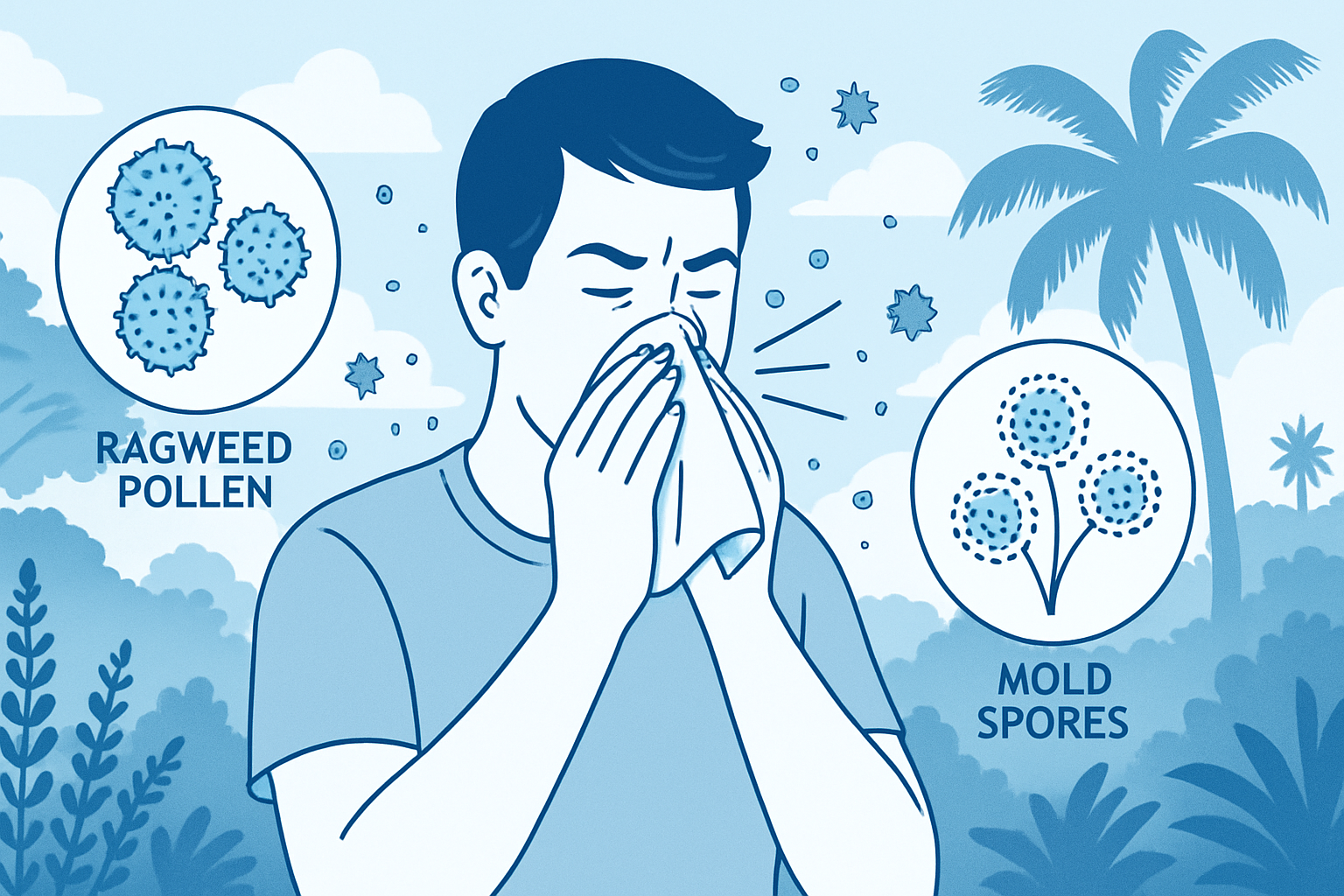
- Animal dander (scales of shed skin)
- The presence of water, sunlight, or extreme temperatures
- Foods (such as berries, shellfish, fish, nuts, eggs, and milk) (such as berries, shellfish, fish, nuts, eggs, and milk)
- Itchy bug bites
- Antibiotics (penicillin and sulfa medications), nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen and naproxen, and blood pressure medicines are examples of drugs that can cause an allergic reaction in some people (ACE inhibitors)
- Pollen
Hives and Angioedema
can also appear with an infection or other sickness, like autoimmune disorders such as lupus, leukemia, and lymphoma.
There are also types of food that trigger abdominal angioedema episodes, such as:
- tomatoes,
- bread,
- shrimp,
- pineapple,
- strawberries,
- milk,
- kiwis,
- tree nuts,
- garlic,
- cheese,
- apples,
- onions,
- leeks,
- bananas,
- citrus fruits,
- fish,
- green salads,
- alcohol,
- chicken.
Types of Angioedema
There are several different types of Angioedema. The condition could be broken down into several unique subtypes by certain organizations, with symptoms of each subtype differing. In general, the different types of Angioedema generally include the following:
1. Idiopathic Angioedema
Unknown causes of Angioedema are known as idiopathic Angioedema. Symptoms may include swelling on your face, hands, trunk, arms, and legs. Some people also have problems with their immune systems and their emotions.
2. Hereditary Angioedema
More commonly referred to as HAE, hereditary Angioedema is a condition in which a person inherits an increased risk of experiencing severe allergic reactions. This risk can be passed down from one generation to the next. One parent with the gene for HAE is enough for you to get it.
There are three forms of this Angioedema, and they are all connected in some way to the amount of C1 protein and/or C1 esterase inhibitor present in the blood, as
follows:
Type I HAE is the most common type of HAE. It is caused when your blood doesn't have enough
C1 esterase inhibitors (C1-INH). Low protein levels and the function of C1-INH mark type I HAE. It is usually passed down in an
autosomal dominant way.
Type II HAE. A lack of C1-INH also causes Type II HAE. This type is
marked by normal to high levels of antigenic C1-INH, which is a mixture of functional and nonfunctional gene products. Most of the time, this is also passed down in an autosomal dominant way.
Type III HAE, which
mostly affects women, is rare and newly recognized. It is not caused by C1-INH deficiency, but mutations in genes that influence the clotting system or bradykinin pathway can increase bradykinin production, which dilates and leaks blood vessels. Type III HAE is frequently autosomal dominant.
3. Acute Allergic Angioedema
This type of Angioedema could be the one you know best. It happens when you have an allergic reaction to something you have touched. This could be a food or drink, a medicine you took, or something you felt (as in items made with natural rubber latex). This Angioedema can also happen if a bug or spider bites you.
4. Non-Allergic Drug Reaction
This kind of Angioedema doesn't manifest immediately after taking medicine. Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors, also called ACE inhibitors or ACEIs, are the drugs that most often cause this reaction.
5. Acquired C1 Inhibitor Deficiency
Angioedema happens when you don't have enough C1 inhibitors, but it's not something you're born with. This condition can cause life-threatening asphyxiation due to laryngeal edema.
6. Vibratory Angioedema
The swelling, in this case, is caused by repeated shaking. You can get these while riding a motorcycle, running, jogging, getting a vigorous massage, or doing other things.
Vibratory Angioedema is a
chronic inducible urticaria, a similar but rare condition in which hives are caused by things like cold, heat, water, pressure, or vibrations. This happens over and over and lasts for about six weeks.
Angioedema Treatments
Angioedema will not require treatment if it is moderate or localized. Swelling that affects your lips, tongue, or throat usually requires hospitalization.
Treatments for Angioedema
include:
- Detecting and avoiding the root cause - if a medication is believed to be the culprit, you can be prescribed a new one.
- Antihistamine medicine, such as cetirizine, fexofenadine, or loratadine.
- Tablets or steroids like prednisolone.
Additionally, medication will be required to prevent the recurrence of hereditary Angioedema if you have it. You could be subjected to periodic reviews to determine whether or not your treatment is effective.
If your symptoms worsen, you should return to the hospital for more tests and treatment.
Get Help From the Specialists!
If you're looking for an "allergy doctor near me" or an "allergist in Florida," Dr. Sabharwal, our board-certified allergist, and immunologist is an expert in detecting and treating children and adult allergies.
She and our skilled team of allergy specialists take pride in being updated on the latest treatments and diagnostic methods to ensure the accurate diagnosis and treatment of your Angioedema:
To contact Allergy Affiliates and arrange an appointment, please click
here.